AI Platforms and Data Privacy: DeepSeek vs. ChatGPT vs. Perplexity vs. Anthropic
Your AI Chatbot Might Be Spying on You—Here’s the Proof
As AI-powered tools continue to revolutionize how we work everyday, data privacy concerns remain at the forefront. Many users wonder: What kind of data do these platforms collect? How is it stored? Who has access—governments, third parties, or advertisers?
In this blog, I have tried to compare the data collection, storage, and sharing policies of DeepSeek, ChatGPT (OpenAI), Perplexity, and Anthropic, with a special focus on government and third-party access to user data. It also incorporates recent insights highlighting DeepSeek’s collection of biometric data, which introduces additional security risks.
DeepSeek
Data Collected
Personal Information:
Name, email, phone number, date of birth.
User Input:
Chat logs, uploaded files, and user feedback.
Technical Data:
Device model, OS, keystroke patterns, IP address.
Usage Data:
Feature usage and actions taken.
Cookies & Tracking:
Uses cookies and other tracking mechanisms.
Payment Data:
Collected for transactions.
Biometric Data:
Keystroke patterns and rhythms—which can be used to uniquely identify individuals based on their typing behavior.
Why Is Biometric Data Collection Risky?
Unlike passwords, biometric data cannot be changed if compromised.
DeepSeek stores all collected information on servers located in China, making this data subject to Chinese cybersecurity laws.
This raises major concerns about permanent digital fingerprints being stored and potentially accessed by unauthorized parties.
Data Storage & Security
Data is stored on servers in China, subject to the country’s cybersecurity laws.
Risk: Chinese data laws require companies to provide user data to government agencies upon request.
Government or Third-Party Access
Chinese Government Access: Yes
China's Cybersecurity Law (2017) and Data Security Law (2021) allow the government to request user data from companies operating within China.
Third-Party Access:
No official mention of sharing with third-party advertisers, but data may be shared with business partners or government agencies as per local regulations.
Privacy Concern
If you are outside of China, using DeepSeek means your data is subject to Chinese regulations, where government access is legally mandated. This is a significant risk for those concerned about surveillance or regulatory compliance in other jurisdictions. Additionally, biometric data collection introduces long-term security concerns, as leaked or misused biometric identifiers cannot be reset like passwords.
ChatGPT (OpenAI)
Data Collected
Personal Information:
Name, email, phone number, payment details.
User Input:
Prompts, uploaded files, conversations.
Technical Data:
IP address, browser type, device information.
Usage Data:
Features used, time spent on the platform.
Data Storage & Security
Data is stored in GDPR-compliant regions, including the U.S. and Europe.
OpenAI emphasizes privacy protections, especially for enterprise users who can opt out of data being used for model training.
Government or Third-Party Access
Government Access: Possible under U.S. law
U.S. CLOUD Act (2018) allows U.S. authorities to request data from companies based in the U.S.
OpenAI may be required to hand over data under legal warrants or subpoenas.
Third-Party Access: No
OpenAI does not share user data with advertisers or third parties for marketing.
Privacy Concern
While data is not shared for advertising, U.S. government agencies may request access under the CLOUD Act. However, OpenAI’s policies indicate no voluntary sharing with governments or third parties outside of legal requirements.
Perplexity AI
Data Collected
Personal Information:
Email, hashed identifiers.
User Input:
Search queries and responses.
Technical Data:
IP address, cookies, interaction logs.
Data Storage & Security
Data is likely stored in the U.S. but subject to business agreements with third parties.
Uses tracking technologies, including mobile identifiers and cookies.
Government or Third-Party Access
Government Access: Yes, under U.S. CLOUD Act
As a U.S.-based company, Perplexity AI must comply with government data requests.
Third-Party Access: Yes
Perplexity explicitly shares user data with advertisers and business partners.
This includes mobile identifiers, hashed email addresses, and cookie identifiers for ad targeting.
Privacy Concern
Unlike OpenAI, Perplexity openly shares data with advertisers and third-party partners, making it one of the least private AI platforms.
Anthropic (Claude)
Data Collected
Personal Information:
Name, email, contact details.
User Input:
Chat conversations and uploaded files.
Technical Data:
Device type, browser info, location data.
Data Storage & Security
Data is stored in GDPR-compliant regions.
Anthropic prioritizes AI safety and privacy, avoiding advertiser-based monetization.
Government or Third-Party Access
Government Access: Yes, under U.S. CLOUD Act
Like OpenAI and Perplexity, Anthropic can be compelled to provide user data to U.S. government authorities.
Third-Party Access: No
Data is not shared with advertisers or business partners.
Privacy Concern
Anthropic is comparable to OpenAI in privacy practices, though legal challenges over copyrighted training data raise concerns about how its AI models were initially built.
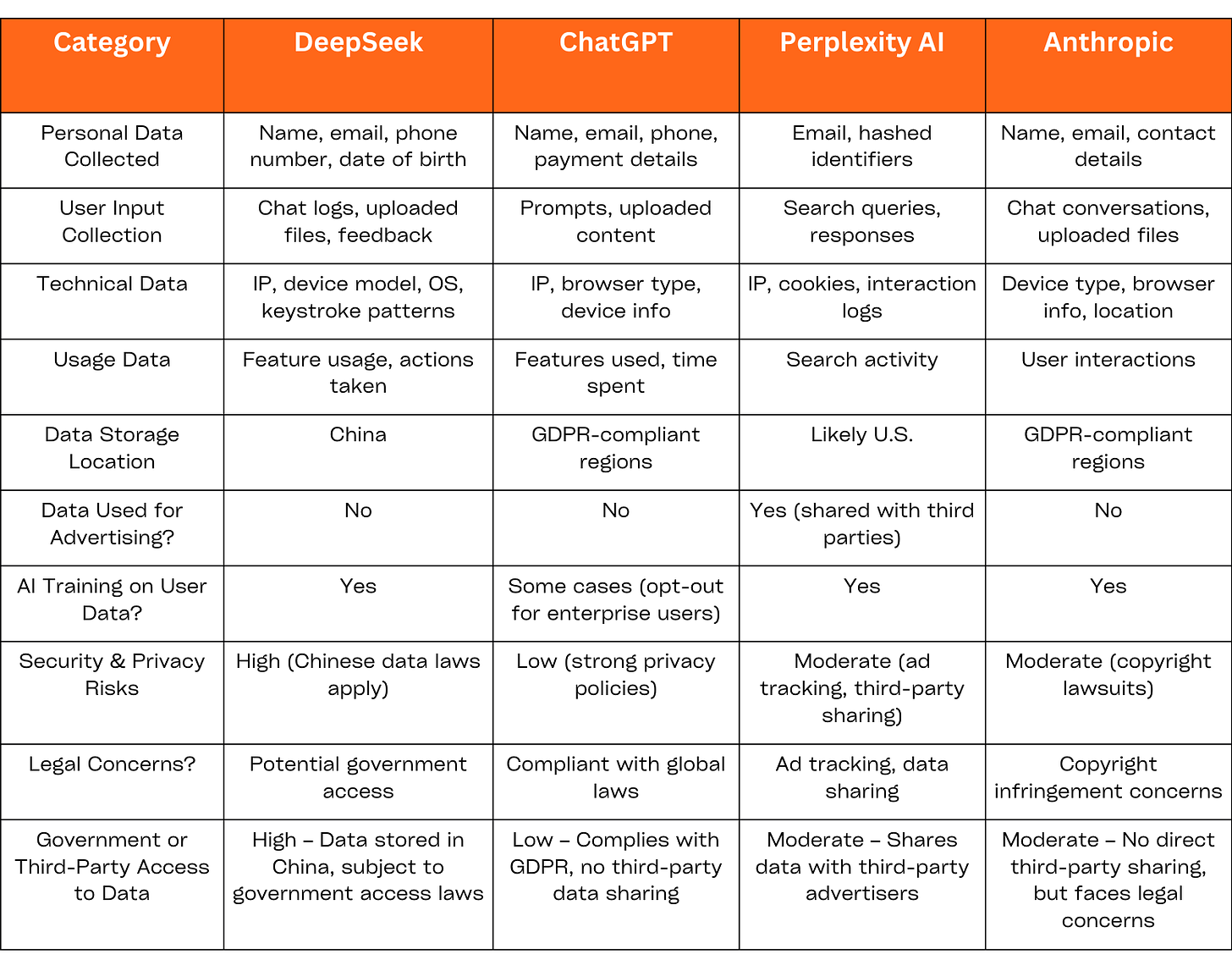
Comparison Table
Key Takeaways
DeepSeek has the highest risk of government access, as China’s data laws allow authorities to request access to user data at any time.
ChatGPT (OpenAI) offers the strongest privacy protection, as it does not share data with advertisers and follows strict global privacy laws.
Perplexity AI shares data with advertisers and business partners, making it less private than the other platforms.
Anthropic (Claude) does not sell data but has faced lawsuits related to copyrighted content usage.
If privacy is your top concern, ChatGPT (OpenAI) and Anthropic are the best choices, while DeepSeek poses the greatest risks due to potential government access to stored data.